Difference between revisions of "Internet Security"
(→Problems) |
(→Problems) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
As a first step this site will focus on the security of the user devices, in particular with the mobile smartphone both as a platform as the apps that work on that platform operating together as a user agent. This can be combined later in the project with any service providers that directly focus on user agent functions. | As a first step this site will focus on the security of the user devices, in particular with the mobile smartphone both as a platform as the apps that work on that platform operating together as a user agent. This can be combined later in the project with any service providers that directly focus on user agent functions. | ||
| − | The complexities that can be faced in securing the operation of a user agent is well exhibited in this [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7tMyAI7h878 Louisiana Wallet example] which can both hold the mobile driver's license of the holder, but also act as a verifier of other's license as might be encountered if the holder were a gig worker that had to | + | The complexities that can be faced in securing the operation of a user agent is well exhibited in this [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7tMyAI7h878 Louisiana Wallet example] which can both hold the mobile driver's license of the holder, but also act as a verifier of other's license as might be encountered if the holder were a gig worker that had to verify the age of the recipient of, for example, a delivery of wine to the household. |
==Solutions== | ==Solutions== | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 17 September 2021
Full Title or Meme
Internet Security appears to be an oxymoron as a network of networks could not be expected to harbor any underlying security model. So what ever security is to exist will need to be layered over the internet.
Context
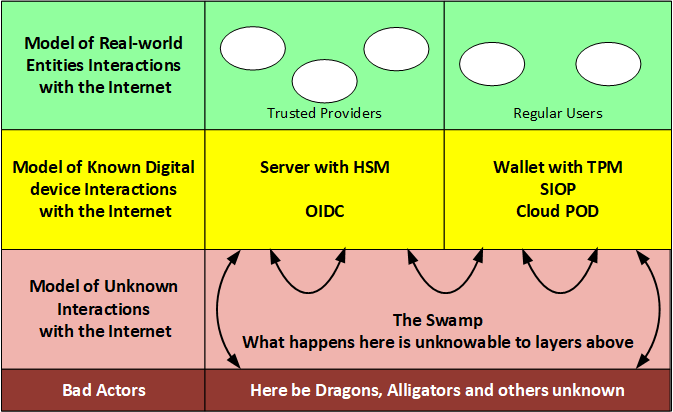
While the Internet may appear to be just a swamp of bad actors, as shown below, we can discuss security for two broad categories of real-world actors, the service providers and the human users. The follows graphic shows those two real-world actors, together with their digital internet manifestations and the interactions among the actors.
- User to user
- User to Trusted Service Provider
- Service Prover to Service Provider
- Bad actor attacking users
- Bad actors attacking service providers.
- There are two interfaces of interest, (1) at the user's agent, and (2) at the provider endpoint access to the internet.
- There is one source of trust of interest: a list of trusted service providers either in the user head or in the user's agent.
- All security is inherent in the messages that are received from the swamp, so the structure and content of these messages, combined with the security of the digital devices, procedures and programs used by the real-world entities will be the entire determinate of the security of the site.
- Also see the wiki page on Internet Bill of Rights
Problems
The shear volume of devices, software and procedures used at any digital endpoint makes securing the entirety of the endpoint very difficult. Attempts to focus on the protocols or data structures used in the interchanges over the internet have proved to be inadequate to the task.
As a first step this site will focus on the security of the user devices, in particular with the mobile smartphone both as a platform as the apps that work on that platform operating together as a user agent. This can be combined later in the project with any service providers that directly focus on user agent functions.
The complexities that can be faced in securing the operation of a user agent is well exhibited in this Louisiana Wallet example which can both hold the mobile driver's license of the holder, but also act as a verifier of other's license as might be encountered if the holder were a gig worker that had to verify the age of the recipient of, for example, a delivery of wine to the household.