Difference between revisions of "QR Code"
From MgmtWiki
(→Problems) |
(→Mastercard) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Full Title or Meme== | ==Full Title or Meme== | ||
| − | A [[QR Code]] is just a specific two | + | A [[QR Code]] is just a specific two dimensional extension of a bar code. |
==Context== | ==Context== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Problems== | ==Problems== | ||
| + | * [https://www.forbes.com/sites/davidbirch/2024/02/28/the-ftc-is-concerned-about-qr-codes-and-so-should-you-be The FTC Is Concerned About QR Codes] 2024-02-28 for example car parks with a payment QR code are being pasted over with scam sites that will be happy to take your money. | ||
* [https://www.idtheftcenter.org/post/qr-code-security-threats-begin-to-grow-as-digital-barcode-popularity-rises/ QR Code Scams Grow as Digital Barcode Popularity Rises] 2024-01-03 | * [https://www.idtheftcenter.org/post/qr-code-security-threats-begin-to-grow-as-digital-barcode-popularity-rises/ QR Code Scams Grow as Digital Barcode Popularity Rises] 2024-01-03 | ||
| − | * A report by Vint Cerf<ref>Vint Cert ''On QR Codes and | + | * A report by Vint Cerf<ref>Vint Cert ''On QR Codes and Safety'' '''CACM 66''' No. 2 p. 7 (2022-02)</ref> shows a common disconnect between the holder of the [[Smartphone]] that processes the app, the site where the holder is and the owner of the website where the holder enters private information. The necessity for informed consent by the holder is a strong binding between the site getting the data with the transaction that the user is asked to complete. It is in restaurants where this is a common occurrence for the restaurant to contract with a [[Third Party]] service provider, who will be the data collector for the transaction. |
* [https://www.theverge.com/2022/1/12/22879728/phishing-scam-parking-meter-qr-code-austin-san-antonio A 2022-01-22 phishing scam to watch out for: fraudulent QR codes on parking meters] | * [https://www.theverge.com/2022/1/12/22879728/phishing-scam-parking-meter-qr-code-austin-san-antonio A 2022-01-22 phishing scam to watch out for: fraudulent QR codes on parking meters] | ||
* See other attacks on the wiki page [[Wallet#QR Codes]] and the wiki page [[Quishing]]. | * See other attacks on the wiki page [[Wallet#QR Codes]] and the wiki page [[Quishing]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Mastercard== | ||
| + | [[Point of Sale]] QR presentation from the Merchant ([[Veryifier]]) in lieu of the physical card. | ||
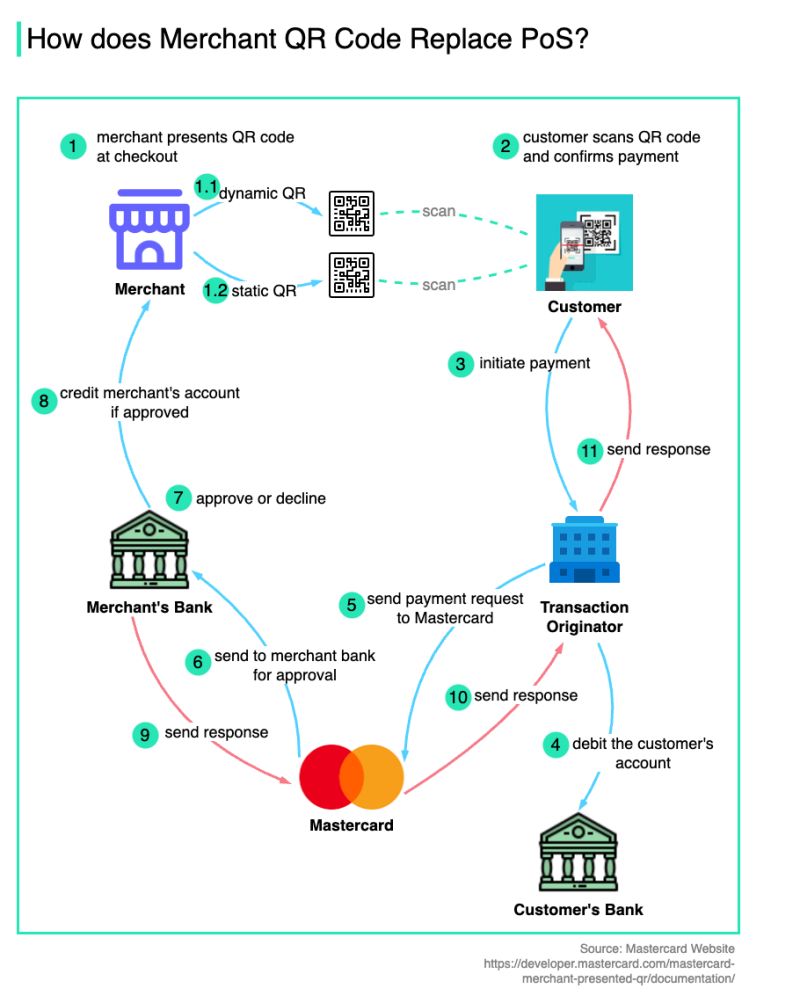
| + | |||
| + | The diagram below shows how Mastercard MPQR (Merchant Presented QR) works. There is 𝐧𝐨 𝐏𝐨𝐒 𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐥 𝐨𝐫 𝐩𝐡𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐜𝐚𝐫𝐝 involved. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Step 1: The merchant presents its QR code at checkout. | ||
| + | There are 𝐭𝐰𝐨 𝐭𝐲𝐩𝐞𝐬 of QR codes: | ||
| + | - 𝐃𝐲𝐧𝐚𝐦𝐢𝐜: the code is generated for each transaction and includes the payment amount | ||
| + | - 𝐒𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐜: the code is used for all transactions | ||
| + | * Step 2: The customer scans the QR code using a mobile app and confirms the payment. | ||
| + | * Step 3: The payment app sends transaction data to the transaction originator to initiate MPQR payment. | ||
| + | * Step 4: The transaction originator debits the customer’s account in the customer’s bank. | ||
| + | * Steps 5 and 6: The transaction originator sends a payment request to the Mastercard network. Mastercard routes the payment request to the merchant’s bank. | ||
| + | * Steps 7 and 8: The merchant’s bank approves or declines the request. If it is approved, the merchant’s bank credits the merchant’s account. | ||
| + | * Steps 9 - 11: The payment response is sent back all the way to the mobile app. | ||
| + | [[File:QR mastercard.jpg]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:41, 22 August 2024
Full Title or Meme
A QR Code is just a specific two dimensional extension of a bar code.
Context
- Used on Web Sites and physical sites to carry URLs and similar encoded Identifiers.
- Is not proposed as a cure-all for places where fully digital transmission of information is not trusted or not possible, or as a fall back for digital device not functioning correctly.
- It is often proposed as a solution to digital exchanges where a radio signal is not possible.
Problems
- The FTC Is Concerned About QR Codes 2024-02-28 for example car parks with a payment QR code are being pasted over with scam sites that will be happy to take your money.
- QR Code Scams Grow as Digital Barcode Popularity Rises 2024-01-03
- A report by Vint Cerf[1] shows a common disconnect between the holder of the Smartphone that processes the app, the site where the holder is and the owner of the website where the holder enters private information. The necessity for informed consent by the holder is a strong binding between the site getting the data with the transaction that the user is asked to complete. It is in restaurants where this is a common occurrence for the restaurant to contract with a Third Party service provider, who will be the data collector for the transaction.
- A 2022-01-22 phishing scam to watch out for: fraudulent QR codes on parking meters
- See other attacks on the wiki page Wallet#QR Codes and the wiki page Quishing.
Mastercard
Point of Sale QR presentation from the Merchant (Veryifier) in lieu of the physical card.
The diagram below shows how Mastercard MPQR (Merchant Presented QR) works. There is 𝐧𝐨 𝐏𝐨𝐒 𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐥 𝐨𝐫 𝐩𝐡𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐜𝐚𝐫𝐝 involved.
- Step 1: The merchant presents its QR code at checkout.
There are 𝐭𝐰𝐨 𝐭𝐲𝐩𝐞𝐬 of QR codes: - 𝐃𝐲𝐧𝐚𝐦𝐢𝐜: the code is generated for each transaction and includes the payment amount - 𝐒𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐜: the code is used for all transactions
- Step 2: The customer scans the QR code using a mobile app and confirms the payment.
- Step 3: The payment app sends transaction data to the transaction originator to initiate MPQR payment.
- Step 4: The transaction originator debits the customer’s account in the customer’s bank.
- Steps 5 and 6: The transaction originator sends a payment request to the Mastercard network. Mastercard routes the payment request to the merchant’s bank.
- Steps 7 and 8: The merchant’s bank approves or declines the request. If it is approved, the merchant’s bank credits the merchant’s account.
- Steps 9 - 11: The payment response is sent back all the way to the mobile app.
References
- ↑ Vint Cert On QR Codes and Safety CACM 66 No. 2 p. 7 (2022-02)