Difference between revisions of "Verifier"
From MgmtWiki
(→Context) |
(→Context) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Context== | ==Context== | ||
| − | * | + | * The traditional name for an entity that needs validated data is a [[Relying Party]]. A [[Verifier]] may be a [[Relying Party]] or only a process that performs a function for one. |
* Verification is the process for determining whether or not an applicant fulfills the requirements or specifications established - a definition derived from the MITRE Systems Engineering Guide.<ref>MITRE https://www.mitre.org/publications/systems-engineering-guide/se-lifecycle-building-blocks/test-and-evaluation/verification-and-validation</ref> | * Verification is the process for determining whether or not an applicant fulfills the requirements or specifications established - a definition derived from the MITRE Systems Engineering Guide.<ref>MITRE https://www.mitre.org/publications/systems-engineering-guide/se-lifecycle-building-blocks/test-and-evaluation/verification-and-validation</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:12, 1 June 2022
Full Title or Meme
In this wiki the common therm for a Verifier is a Relying Party. The distinction seems to be moot.
Context
- The traditional name for an entity that needs validated data is a Relying Party. A Verifier may be a Relying Party or only a process that performs a function for one.
- Verification is the process for determining whether or not an applicant fulfills the requirements or specifications established - a definition derived from the MITRE Systems Engineering Guide.[1]
Problems
- The term Verifier could be limited to just the role played by any Entity in assuring that the data received meets its own criteria for acceptance.
- Some verticals, like finance and health, are highly regulated and typically require that their data controllers are certified for conformance with very restrictive regulations. Others have lighter regulation like the US Federal Trade commission.
- In all cases the verifier will be given a set of policies that they apply to Claimants seeking access. In a world where policies can change will little notice, it behooves the Verifier to create a Policy-Based Access Control applications that does not require reprogramming of the application to meet changing policies.
Solutions
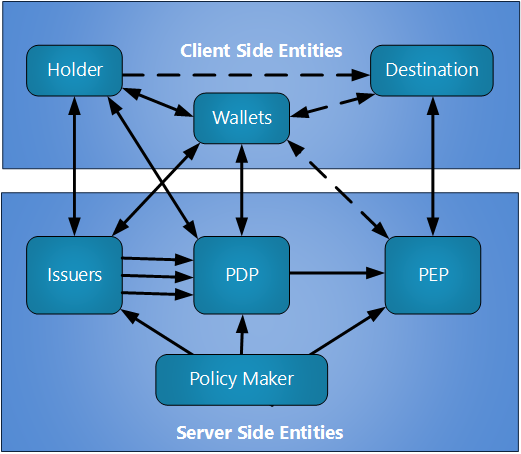
For this wiki we break the Verifier into two roles from SAML:
- PDP = policy definition point
- PEP = policy enforcement point